Data classification is the process of categorizing data based on its sensitivity, importance, or other criteria. This classification helps organizations manage and protect their data more effectively by assigning appropriate levels of security and access controls. Data classification helps ensure that sensitive or critical information receives the necessary protection, while less sensitive data may have fewer restrictions.
Big announcements. Bold innovation.
See how to drive resilience everywhere: across AI, cloud, and identity.
Cohesity data classification
Data is everywhere, and your backups are where everything comes together. Cohesity gives you visibility, context, and control over your sensitive data, helping you minimize risk and speed up your response to data loss.
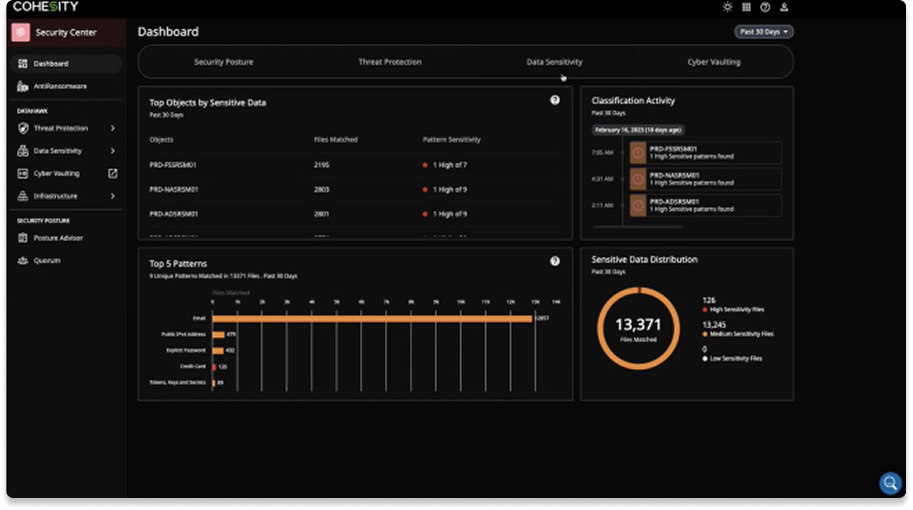
Identify the severity of an attack
When ransomware attacks, do you know what sensitive data was affected? Classify sensitive data, including personal identifiable information (PII), using our highly accurate, ML-based engine. Understand sensitive data proliferation or invoke classification on anomalies for sensitive data impact analysis.
Know your risk
Bring structure to data sprawl by uncovering sensitive, regulated, and high value data and reduce the risk of data exposure from cyberattacks or insider threats.
Accelerate compliance
Classify personal, sensitive, and regulated data to enable mapping to frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI.
Understand the impact of cyberattacks
Understand how a cyberattack will impact your organization by quickly identifying the data that was lost or stolen, allowing you to prioritize your response.

Cohesity CERT (Cyber Event Response Team)
Respond faster, recover smarter—because your business can't afford downtime
- Minimized downtime and data loss: Expert incident response with robust recovery tools dramatically reduces the risk of data loss so your business can recover faster.
- Rapid response to incidents: Cohesity CERT immediately steps in to help you contain the damage and initiate recovery.
- Strategic partnerships: We’ve partnered with the world’s leading cybersecurity incident response firms, so you have what you need to respond to cyberattacks.
Commonly asked data classification questions
Data classification can vary based on the specific needs and requirements of an organization. However, some common types of data classification include:
1. Regulatory Classification: Categorizes data according to regulatory requirements. For example, data may be classified as sensitive personal information under regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or protected health information under HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
2. Confidentiality Classification: Is based on the level of confidentiality or sensitivity. This classification typically includes categories such as public, internal use only, confidential, and highly confidential.
3. Criticality Classification: Data may be classified according to how critical it is to the organization's operations or mission. For example, critical data may include financial records, intellectual property, or trade secrets.
4. Accessibility Classification: Categorizes data based on who should have access to it. For instance, data may be classified as accessible to all employees, restricted to specific departments or teams, or limited to certain individuals with specific permissions.
5. Lifecycle Classification: Is based on the lifecycle stage, such as active, archival, or obsolete. This classification helps organizations manage data storage, retention, and disposal effectively.
6. Format Classification: Is based on its format or structure, such as text, images, audio, video, and structured or unstructured data. Different formats may have varying security requirements and handling procedures.
7. Location Classification: Is based on its physical or geographical location, such as on-premises servers, cloud storage, or mobile devices. This classification helps organizations implement appropriate security measures and data access controls for different locations.
8. Value Classification: Is based on its value to the organization, such as high-value assets, moderate-value assets, or low-value assets. This classification helps prioritize security measures and resource allocation.
Data classification is essential for compliance with regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, as well as for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. It also helps organizations prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources effectively based on the importance of different types of data.

Ready to get started?
Start your 30-day free trial or view one of our demos.